Bopitiya dump stirs up garbage danger, anger

In its haste to dump garbage anywhere but Meethotamulla following the deaths and devastation on April 12, the Government is stirring up more anger across the city.
Residents of Bopitiya are up in arms over the garbage being dumped in Muthurajawela, a part of a wildlife sanctuary.
Residents and environmentalists say the area has been contaminated after several days of garbage dumping by the Colombo Municipal Council.
The Director General, Department of Wildlife Conservation, W. S. K. Pathiratna said yesterday, the dumping had begun while he was out of the country.
Residents complain that the garbage was dumped after a person had claimed ownership of the site.
They said they built their homes bordering the buffer zone of the Muthurajawela sanctuary and had requested approval from the Department of Wildlife Conservation, Sri Lanka Land Reclamation and Development Corporation, and the Agrarian Services.
They say approval had not been sought from the Central Environmental Authority before hauling solid waste to Bopitiya.
During a visit, the Sunday Times saw how people had blocked the narrow entrance to the lane of a housing scheme leading to the dumping site. Police were present.
Within the land, backhoes were seen excavating sand, while a part of the site was being used to dump garbage.
Rev Father Dinush Gayan, assistant parish priest of Bopitiya Church told the Sunday Times that about 300 tonnes of non-biodegradable waste are dumped in a single day.
He said that even when the Agrarian Services requested documents as well as environmental impact assessments, neither the owner of the site nor the government officials could provide them.
Rev Gayan said goons associated with the site owner disrupted a silent protest.
K.L Newton Perera, a lawyer who is also a resident of Nugape, Muthurajawela said some people are using the garbage to fill the land.
Mr Perera said the Meethotamulla dump also was created on marshy land.
“Bopitiya too is included to the Muthurajawela sanctuary and the dump site is also in a watery, marshy soil which stays wet during the dry seasons,’’ he said.
Anil Lankapura Jayamaha, the president of the Organisation for protecting the Muthurajawela Sanctuary, said that the government was dumping garbage by relying on the ownership claims of a person.

“The muddy soil and the waterways which people use for bathing, drinking and fishing, will be poisoned and cause health issues,’’ he said.
He said criminal gangs have moved in to extort money from garbage lorries, just as it was in Meethotamulla.
An official of the Agrarian Services, said 40 foot craters have been dug to dump waste.
The officer said she and officials wrote to President Maithripala Sirisena and the Colombo Municipal Commissioner, and were planning to go to court.
Meanwhile, Land Reclamation chairman, Asela Iddawella, said the Megapolis Ministry and local government offices of Wattala have proposed a waste dump.
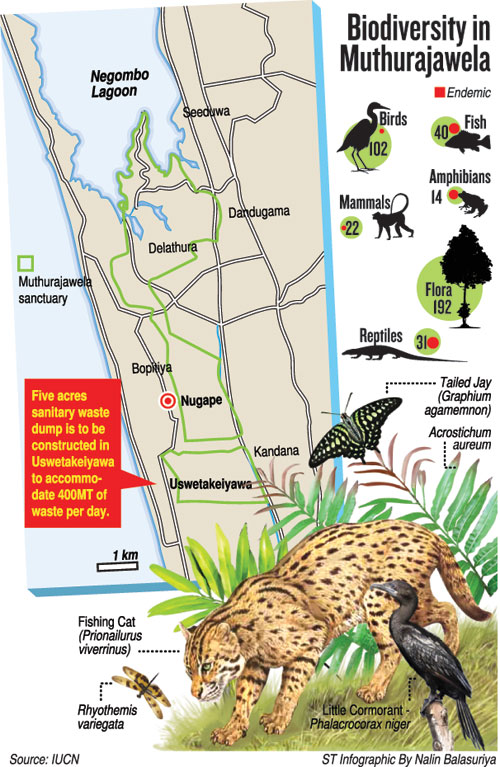
The cabinet this week approved a recommendation for a site to manage 400 metric tonnes of waste per day on a five-acre site in the Muthurajawela area under the Wattala Divisional Secretary.
Mr Iddawela explained that the land at Muturajawela will be used to create an electric power plant, while another land will be used as a sanitary disposal site.
“The plant will create power from 500 tonnes [of waste] per day while a business model garbage dump will also be erected,’’ he said.
He said the waste-to-electricity plant will be operational after three years or a minimum of two years, while the sanitary land fill will take over 18 months.
He said the President also had asked that the engineering assessment and environmental impact assessment be done while the project continues.
The Director General of the Central Environmental Authority, K.H Muthukudarachchi said that the Megapolis and Western Development Ministry was carrying out garbage management programmes.

He said the CEA had done environmental impact assessments for two projects at Muthurajawela, undertaken by the Ministry of Megapolis and local councils.
He said garbage from Colombo will be dumped at Muthurajawela, Karadiyana and Aruwakkalu.
Environmentalist of the Biodiversity Conservation and Research Circle, Supun Lahiru Prakash, said that sanitary fillings are done after recycling various materials and by burying the most toxic waste.
He said the garbage will contaminate the waterways which support the bio diversity of the sanctuary.
He claimed that the private land in Bopitiya is within the vicinity of the sanctuary and the dump has caused damage already. He also warns of the flooding threat.
Mr Prakash said that the government move tramples on laws including wildlife legislation and also disregards a court order.
Source – 30/04/2017. The Sunday Times, See more at – http://www.sundaytimes.lk/170430/news/bopitiya-dump-stirs-up-garbage-danger-anger-238777.html

Pinnawala Elephants to be made available to institutions and individuals
Cabinet has approved a proposal to make available elephants from the Pinnawala Elephant orphanage and National Zoological gardens to individuals and institutions.
A statement on the decision (Document no 60) said “maintenance of the present number of 88 elephants in a restricted land area of 30 acres at Pinnawala has become a difficult task.”
As such a proposal has been put forward by Minister of Wildlife and Sustainable Development Gamini Jayawickrama Perera, “to provide some elephants to individuals and religious places under definite conditions.”
The Cabinet has approved Mr. Perera’s proposal which would permit the adoption of baby elephants to be adopted by individuals and religious places under specific conditions.
The proposal was approved by Cabinet and recommendations on issuing orders for providing elephants for Peraheras, regularizing registration of domesticated elephants and ensuring their protection were also approved.
Source – 27.04/2017, Times Online, see more at – http://www.sundaytimes.lk/article/1020725/pinnawala-elephants-to-be-made-available-to-institutions-and-individuals

Sri Lanka overturns ban on adopting baby elephants as orphanage get overcrowded
Apr 26, Colombo: Sri Lanka has said on Wednesday it would allow individuals and temples to adopt baby elephants under definite conditions overturning a ban on adoptions.
The cabinet of ministers approved a proposal tabled by the Minister of Sustainable Development and Wildlife Gamini Jayawickrama Perera to provide some elephants to individuals and religious places under definite conditions.
The Minister has pointed out that maintenance of the present number of 88 elephants in a restricted land area of 30 acres at Pinnawala Elephant Orphanage has become a difficult task.
The Cabinet of Ministers also approved recommendations on issuing orders for providing elephants for Perahera (religious processions), regularizing registration of domesticated elephants and ensuring their protection.
The ban on adopting elephants had led to worries there would not be enough tame elephants for Buddhist pageants, an AFP report said.
“Wildlife conservation is good, but we also need to conserve our cultural pageants,” government spokesman Rajitha Senaratne was quoted as saying.
Senaratne said the government decision had been motivated partly by overcrowding at Pinnawala, which was set up as an elephant orphanage and now runs a successful breeding program.
He said strict conditions would be put in place to ensure the animal’s welfare. Individuals would have to pay 10 million rupees ($66,000) for an elephant, while temples would get them for free.
Last year, Sri Lanka unveiled tougher laws, including a ban on using young elephants for logging and other physical work, as part of a crackdown on cruelty to animals.
Capturing wild elephants is illegal in Sri Lanka where according to official records the population of elephants in the wild is at about 7,500.
Source – 26/04/2017, Colombo Page, See more at – http://www.colombopage.com/archive_17A/Apr26_1493219655CH.php
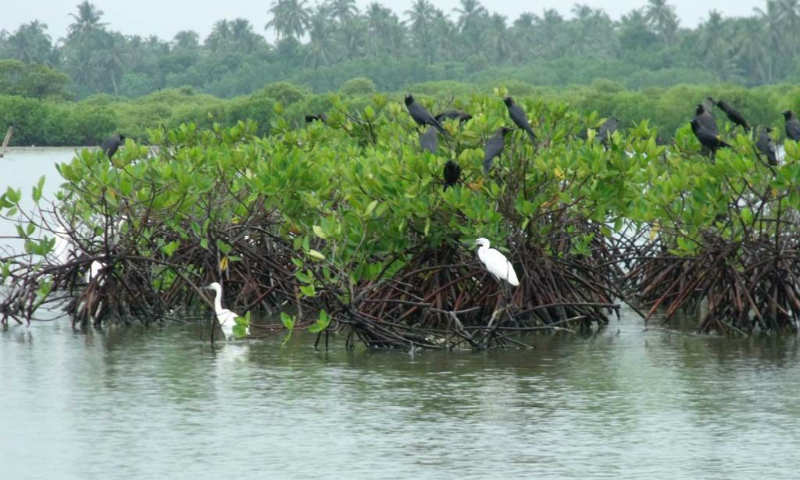

A sanitary landfill at Muthurajawela marsh
Image courtesy: sarathboattours.com
The Cabinet approved the proposal to build a sanitary landfill, at Muthurajawela in Wattala. The garbage collected within Colombo city limits will be dumped there.
The proposal was made by Faiszer Musthapha, the Minister of Provincial Council and Local Government, who added that the project must be implemented as soon as possible.
A Committee was appointed to look into the matter, and they estimated that 400 metric tonnes of garbage can be dumped into the proposed sanitary landfill per day.
Source – 26/04/2017, Front Page, See more at – http://www.frontpage.lk/page/A-sanitary-landfill-at-Muthurajawela-marsh/20027

How San Francisco is Becoming A Zero Waste City
San Francisco has deployed its widely successful solid waste management programme based on the ambitious goal of zero waste by 2020. To ensure that no material goes to landfill or high temperature destruction, the city’s zero waste goal means that products are designed and used according to the principle of highest and best use. Zero Waste also means that discarded materials follow the waste reduction hierarchy: reduce, reuse, and then recycle or compost.
To meet its zero waste goal, San Francisco has used a three-pronged approach that addresses the legal, administrative, and social challenges of waste management reform. Specifically, the City enacted strong waste reduction policies; partnered with Recology, a like-minded materials management company, to innovate new programmes; and created a culture of recycling and composting.
http://www.c40.org/profiles/2013-sanfran

A deadly salamander disease just got a lot scarier
 Europe’s largest and best known salamander species, the fire salamander, is falling victim to a deadly fungus, and new research is making scientists more pessimistic about its future. A 2-year study of a population in Belgium, now entirely wiped out, has revealed that these amphibians can’t develop immunity to the fungus, as was hoped. To make matters worse, it turns out the fungus creates a hardy spore that can survive in water for months and also stick to birds’ feet, offering a way for it to spread rapidly across the continent. Two other kinds of amphibians, both resistant to the disease, also act as carriers for the highly infectious spores.
Europe’s largest and best known salamander species, the fire salamander, is falling victim to a deadly fungus, and new research is making scientists more pessimistic about its future. A 2-year study of a population in Belgium, now entirely wiped out, has revealed that these amphibians can’t develop immunity to the fungus, as was hoped. To make matters worse, it turns out the fungus creates a hardy spore that can survive in water for months and also stick to birds’ feet, offering a way for it to spread rapidly across the continent. Two other kinds of amphibians, both resistant to the disease, also act as carriers for the highly infectious spores.
“This is terrible news,” says geneticist Matthew Fisher of Imperial College London, who studies the fungus but was not involved in the new research. “This isn’t a problem that’s going to go away. It’s a problem that’s going to get worse.”
The pathogen, Batrachochytrium salamandrivorans (Bsal), is a chytrid fungus, a type that lives in damp or wet environments and typically consumes dead organic matter. Bsal infects and eats the skin of salamanders, causing lesions, apathy, loss of appetite, and eventually death. Over the past few decades, a related fungus, B. dendrobatidis (Bd), has struck hard at amphibian populations around the world, particularly in the Americas, Australia, Spain, and Portugal. More than 200 species of frogs and toads are thought to have gone extinct, including many kinds of Costa Rica’s striking stream-breeding toads.
http://www.sciencemag.org/news/2017/04/deadly-salamander-disease-just-got-lot-scarier

Six persons held for engaging dynamite fishing
Six local fishermen who were engaging in illegal fishing practices using dynamite in the sea area off Kuchchaveli arrested by Navy personnel yesterday, Navy said.
Along with the suspects, a dinghy, 2 unauthorized fishing nets, a pair of diving fins, a diving mask, 3 non electric detonators and 100 g of water gel were also taken into naval custody. The suspects, dinghy and other fishing gears were handed over to the Kuchchaveli Police for further investigations.
Source – 24/04/2017, Times Online, See more at – http://www.sundaytimes.lk/article/1020532/six-persons-held-for-engaging-dynamite-fishing
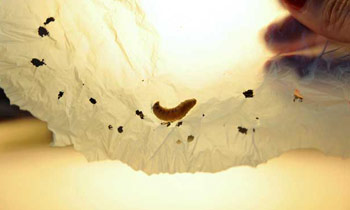
Hungry caterpillar Joins fight against plastic pollution
A moth caterpillar commonly bred to provide fish bait feasts on a notoriously resistant plastic, scientists reported Monday, raising hopes the creature can help manage the global problem of plastic-bag pollution.
“This discovery could be an important tool for helping to get rid of the polyethylene plastic waste accumulated in landfill sites and oceans,” said Cambridge University professor Paolo Bombelli, co-author of a study published in the journal Current Biology.
Polyethylene represents 40 percent of Europe’s demand for plastic products, mostly in the form of packaging and shopping bags. Taking many years to biodegrade, these objects constitute a serious hazard for the environment, especially for sea life, when they are not recycled.
In the European Union, 38 percent of plastic is thrown out in landfills. The promising discovery centers on the wax worm — the name for the caterpillar larva of Galleria mellonella, or greater wax moth. In its pre-caterpillar form, the species is commercially raised as maggots to provide fish bait and aquarium food.
The moth is also a scourge of apiculture, laying its eggs in the precious honeycomb of beehives. The find happened by accident at the home of the study’s lead author, Federica Bertocchini, a biologist at the Institute of Biomedicine and Biotechnology of Cantabria in Spain. Bertocchini keeps beehives as a hobby.
“When I went to clean them for reuse in the spring, they were infested with (wax) worms,” the researcher told AFP. “So I put them in a bag.
Then, after a while, I saw the bag was full of holes and these caterpillars were crawling all around my place.” Startled by the caterpillar’s voracious appetite, Bertocchini and a team from Cambridge University decided to conduct experiments to find out just how much, and how quickly, the pests could consume environmentally harmful plastic. They placed hundreds of the small, yellowish creatures on top of a supermarket plastic bag.
Within 40 minutes, holes began to form. Twelve hours later, the caterpillars had consumed 92 milligrammes (0.003 of an ounce) of the stuff, far swifter than fungus and bacteria would have taken.
In their next test, the biologists confirmed that the larvae fully digest a plastic meal, breaking down its chemical components. Covering a plastic bag with mashed-up caterpillars produced a similar results, suggesting that an enzyme or some other compound was at work. “
The caterpillar produces something that breaks the chemical bond, perhaps in its salivary glands or a symbiotic bacteria in its gut,” Bertocchini said. The answer may lay in the worm’s habitat and eating habits. Growing in bee colonies, the moth larvae feed on beeswax, a digestive process that scientists believe may be similar to breaking down polyethylene. “Wax is a polymer, a sort of ‘natural plastic,’ and has a chemical structure not dissimilar to polyethylene,” Bertocchini suggested.
It remains unclear if a single enzyme or a combination of molecules are responsible for degrading plastic. But biologists hope to identify and reproduce the active agent artificially. “Using million of caterpillars on top of plastic bags would not be feasible,” Bertocchini said.
Manufactured on a large scale, the plastic-degrading substance would, in theory, take the form of an environmentally harmless liquid that could be used in plastic treatment facilities. (NDTV)
Source – 25/04/2017,Dailymirror- See more at: http://www.dailymirror.lk/article/Hungry-caterpillar-Joins-fight-against-plastic-pollution-127738.html#sthash.ZyO2g25o.dpuf
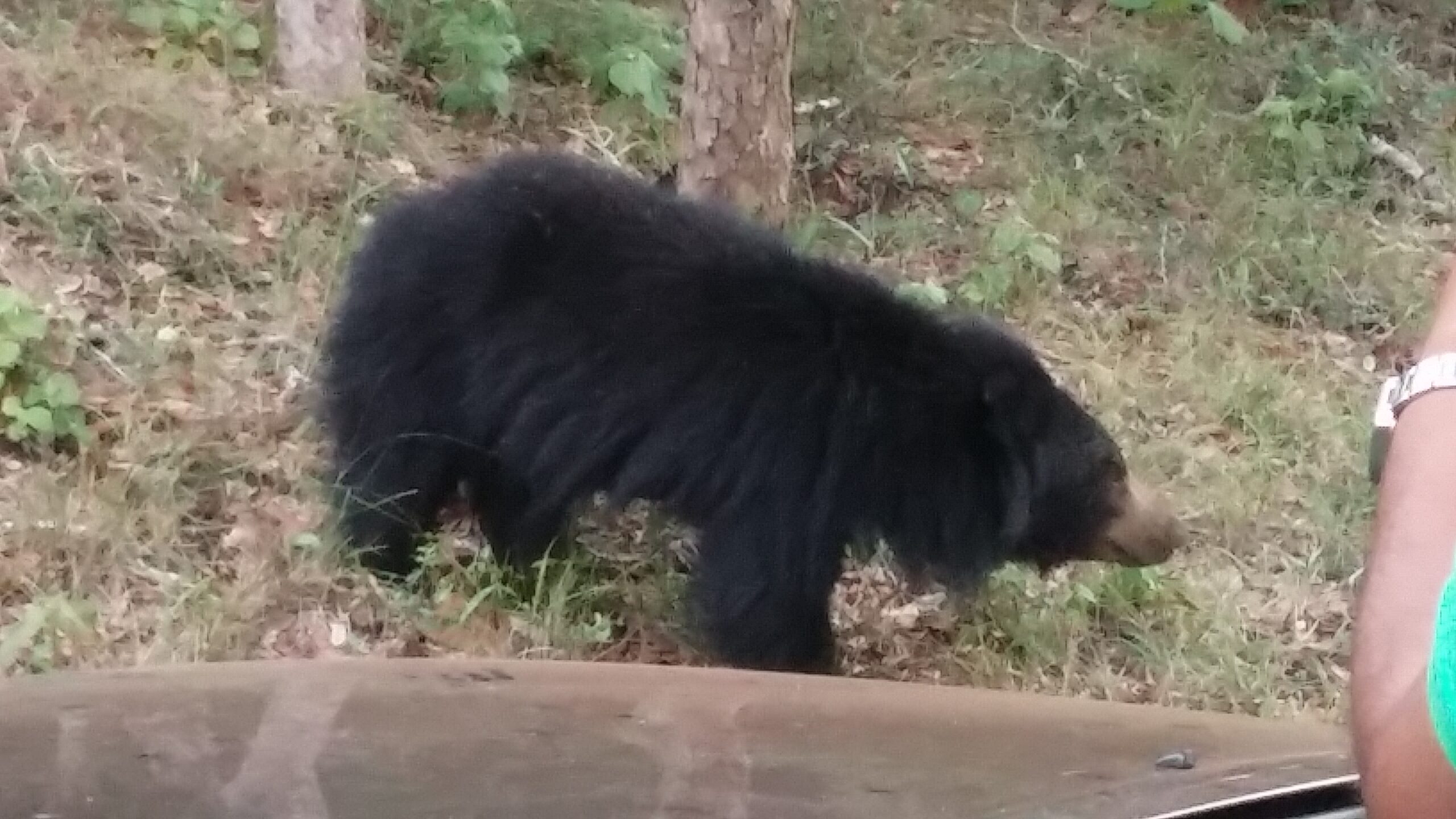

BSL in association with CIC Holdings and BEAR for ESTIMATING THE SLOTH BEAR POPULATION IN WILPATTU NATIONAL PARK
 The Sri Lanka Sloth Bear (Melursus ursinus inornatus) is a subspecies which is endemic to the island nation. The sloth bear is one of the most adversely affected animals due to deforestation and urbanization. As, this species is very sensitive to disturbances, currently it is restricted to the National parks and sanctuaries in the lowlands of the island. Due to prevalent misconceptions among the villagers, the sloth bear has earned the reputation as one of the most dangerous animals in Sri Lanka. It is deliberately avoided by jungle men as the most feared creature in Sri Lanka’s wilds. Even to date, the sloth bears are killed by villagers whenever an opportunity arises, during their forages to the forest to collect honey and other forest products. During the survey several dead sloth bears were found close to villagers, their death was due to gun shots and snares. Sloth bears were reported as abundant during the colonial period, but declined speedily and drastically due to habitat loss and hunting. The colonial sports men used to sit over water holes during the dry season to shoot sloth bears, which come to quench their thirst – sloth bears unlike other large mammals need to have their daily fill of water.
The Sri Lanka Sloth Bear (Melursus ursinus inornatus) is a subspecies which is endemic to the island nation. The sloth bear is one of the most adversely affected animals due to deforestation and urbanization. As, this species is very sensitive to disturbances, currently it is restricted to the National parks and sanctuaries in the lowlands of the island. Due to prevalent misconceptions among the villagers, the sloth bear has earned the reputation as one of the most dangerous animals in Sri Lanka. It is deliberately avoided by jungle men as the most feared creature in Sri Lanka’s wilds. Even to date, the sloth bears are killed by villagers whenever an opportunity arises, during their forages to the forest to collect honey and other forest products. During the survey several dead sloth bears were found close to villagers, their death was due to gun shots and snares. Sloth bears were reported as abundant during the colonial period, but declined speedily and drastically due to habitat loss and hunting. The colonial sports men used to sit over water holes during the dry season to shoot sloth bears, which come to quench their thirst – sloth bears unlike other large mammals need to have their daily fill of water.
In Sri Lanka, population estimates and abundance of the sloth bear is greatly lacking. In order to fill this gap in knowledge and to gather base line data on their population density and home range, the current project was initiated, first in Wilpattu National Park, as it is reported to harbour one of the largest populations of sloth bear, as per a study done in the 1970’s by Eisenberg and Lockhart. This forms the first stage in an island wide study on the Sloth Bear in Sri Lanka.
Our goal is to map, evaluate the population density and composition of sloth bears in Wilpattu National Park and to identify their habitat needs and preferences. The information gained through this study can then be applied island wide in the subsequent strategies and efforts for the conservation of the sloth bear.
The project was initiated on the 3rd of June 2013 with the financial support from CIC Holdings PLC through Biodiversity Sri Lanka. To date over 100 field days have been spent in the wilds of Wilpattu for the said survey and study.

Environmentalists fire warning shots over “senseless” jumbo killing
The elephant being rescued, but soon the she elephant lay dead. Pix by Ramesh Madushanka
A wild elephant is dead – at the hands of the Department of Wildlife Conservation (DWC), the very institution which is supposedly the guardian of these majestic animals.
“When will we ever learn,” is the lament of numerous environmentalists as there were howls of protest not only from them but also the public over this “senseless” killing.
The DWC over-reacted and used excessive force than was necessary, was the consensus among them, as two parallel probes were launched by Wildlife and Sustainable Development Minister Gamini Jayawickrama Perera and the DWC.
The video of the shooting of the cow-elephant in Kombaveittakulam, Omanthai, Vavuniya is heart-rending. Two adult females and their babies had fallen into an agricultural well. Perhaps, a baby fell in first and in their efforts to save it the others fell in too. The two babies were apparently taken out first by the DWC. The agony and the stress of the two bigger elephants, left swimming round and round, attempting to get out of this watery trap is obvious.
Then comes into view, in the eyes of the elephants, what would have been a different threat – a huge orange backhoe, while in the background the so-called rescue personnel including the DWC staff can be heard shouting at the animals. A ‘circus’ seems to ensue thereafter.
In the last moments of her life, the desperation of the cow-elephant, firstly struggling to get up the muddy and slippery slope of the well can actually be felt even through the video. Her futile attempts to charge at the orange monster blocking her escape route into the jungle and finally, the sound of one shot, a cloud of smoke, a second shot and another cloud of smoke and a third shot and a cloud of smoke and as if in slow motion, the majestic elephant collapses and drops dead. Since it is believed that she was a nursing mother, her killing also condemns her baby to death by starvation.
Whether the other elephant was also injured, as a gun-shot seems to be in that animal’s direction as well, remains a mystery.
DWC sources told the Sunday Times that the department was conducting an inquiry and the report was expected early next. When asked for details with regard to the incident, the source said that the well was about 12km off the A9, in a rural area. The rescue operation was carried out at around 9.30 a.m. on Monday (April 17). The elephants had been spotted in the well the previous day. There were two cow elephants and two babies, but the DWC was not certain whether the babies were of those cow elephants.

“There was absolutely no need to shoot dead the elephant which was of little threat to the DWC guard who was on the backhoe,” was the view of experts who analyzed this particular incident and pegged it to a wider issue.
“Elephants charging at vehicles happens not uncommonly and jeeps do get hit in wildlife parks. Raiding elephants often attack tree huts in chenas and elephants break down houses to get at stored grain. Killing an elephant is not considered the appropriate response in any of these instances,” said the Chairman of the Centre for Conservation and Research (CCR), Dr. Prithiviraj Fernando, who has been conducting research on elephants for nearly three decades.
Reiterating that many other measures could have been tried, before shooting dead the elephant, he said that the most logical first reaction should have been — when they saw the animal coming out — was to move the backhoe, which was clearly blocking her pathway to freedom. There seems to have been no thinking or planning before using fire-power to kill.
Even if the backhoe was not moved, the animal could have been diverted from heading towards the backhoe by fire-crackers first and if those did not work, then non-lethal bird-shot from a shot-gun. These are tiny lead pellets which would hit the skin of the elephant and caused pain but not go through and leave huge fatal injuries. The cartridges with large lead balls used in this instance as a first resort were absolutely the wrong ammunition. The DWC guard could have also shot at the body and not made a direct hit at the head of the elephant, the Sunday Times understands.
While the ‘lighter’ measures such as fire-crackers and bird-shot are tried out, another official could stand-by with a rifle to take down the animal if human life is endangered. But killing the elephant should be the very last resort, according to Dr. Fernando. “It should definitely not be the first-line of defence.”
The Wildlife and Nature Protection Society (WNPS), meanwhile, in a statement issued on Thursday night, titled ‘From protector to executioner’ strongly protested against the shooting.
As the oldest conservation organization of its kind, the founder of the initial National Parks and prime facilitator in the setting up of the DWC, the WNPS underscored that this act of needless destruction of a nationally-protected species by those who should be protecting them counters every principle of conservation on which these institutions were established.
“The available video coverage of the incident clearly shows that at no time was human life in danger during the incident and the need to shoot the elephant dead, rather than just frighten it away as has been done before, is called into question. The video also shows another elephant being shot at and falling, though the DWC claims that only one died. The DWC is the main statutory agency set up for the protection of all wildlife, including elephants. If they have now taken to shooting the animals they are supposed to protect, then an already endangered species is doomed to extinction,” it said.
Strongly urging that the two inquiries into this elephant-killing be carried out with a degree of transparency that leaves nothing open for question, the WNPS states that as per the available video footage of the incident, the ‘circus’ that surrounded this tragic killing, highlights alarming lapses in procedure and gaps in the law. They include:
Astoundingly, the DWC does not have an official protocol or procedure to deal with situations like this, the extrication of wild elephants from unguarded irrigation pits/wells, despite it being an all too frequent occurrence of late. Had they done so, the army of onlookers would have been cleared and appropriate measures taken to channel the rescued animals away from the rescuers.
If a human falls into an unguarded well or pit, the person or persons who made the excavation are legally liable for any resulting injury and costs. Yet, when an elephant falls into such a hole, the DWC is not only held liable for its extraction, but has to bear the resulting costs. These wells/channels are often paid for by aid agencies and they should ensure that basic measures are taken not only to prevent elephants and other animals from falling in, but also humans. Those who dig these holes and leave them unguarded should be held liable to pay for the costs of anyone or any animal falling in. Such legal measures, if enforced, would soon result in proper safety measures being implemented for the wellbeing of all – humans and animals.
“It is hoped that this tragedy will result in the DWC and the ministry commencing discussions and consulting elephant and legal experts to formulate a protocol to deal with such situations where the destruction of the animal will be the last resort, rather than the first, trigger-happy choice. It is too late for this unfortunate victim but the world will be watching to see whether justice will prevail in her killing and whether there is any hope for the conservation of the wild elephant under the present political and administrative institutions responsible for their protection and under the law,” the WNPS adds.
Another environmentalist also pointed out that the DWC guard, who shot dead the elephant, has been transferred to a different area, which indicates that the DWC has not acknowledged the fundamental reasoning that the killing was not acceptable. What the right course of action would have been is to send the official on compulsory leave, as the killing of an elephant is against the law of the country, at least until the investigations were concluded. The message from the current actions is that it is acceptable to kill an elephant even though it is an illegal act under Sri Lankan law.
Taking up a press release issued by the Game-guard Union that the guard’s action was justified because the elephant was “on a rampage and the killing was carried out in self-defence”, another environmentalist was quick to point out that the video clearly shows that the ‘rampage’ part was totally untrue.
The implication of such a stance is very dangerous, he said, adding that it promotes the thinking that elephants should be killed and that’s what villagers will do, making the human-elephant conflict take on a different dimension. “We will give villagers an excuse to take the law into their own hands if an elephant damages a home or a tree-hut. The message being told loud and clear, wrongly, is that when faced with an aggressive elephant you should kill it.”
Source – 23/04/2017, The Sunday Times, See more at – http://www.sundaytimes.lk/170423/news/environmentalists-fire-warning-shots-over-senseless-jumbo-killing-238070.html













