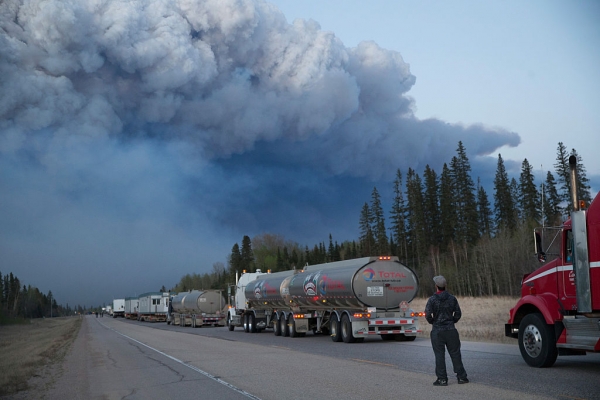

Canada Wildfires Have Grown 200,000 Acres, Thousands Evacuated

(Photo : Scott Olson/Getty Images)
Canadian wildfires have grown over 200,000 acres and many people have been forced to evacuate.
As the fire grew, many people were forced to go into evacuation. On Thursday, the Alberta government said there were more than 1,100 firefighters, 145 helicopters, 138 pieces of heavy equipment and 22 air tankers were sent to fight a total of 49 wildfires, with seven considered out of control.Currently, Candian officials help 8,000 people to airlift from Fort McMurray. The officials are hoping that the motorway to the south will be become safe by Friday so they can help move the remaining 17,000 people, according to BBC.
Luckily, there were no injured people reported. Is climate change the reason for more wildfires?
There are 1.9 billion hectares of boreal forest around the world, and Canada is home to 552 million hectares or 28 per cent of the world’s boreal zone according to Global News. Boreal forest is the largest terrestial biome, is also known as taiga or snow forest that consist mostly of pines, larches, and spruces. These forests are under threat by a climate change because of continues warming of temperature. Currently, boreal forests have already warmed by 0.5 C to 3 C. The continues rising of temperature linked to drier conditions.
According to the latest report of Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), the area of boreal forest burned in North America has doubled over the past 20 years.
The three key ingredients to propagate wildfire weather conditions are hot weather, wind , and low humidity. A warming climate may produce two of the three ingredients. It could be warm air, which is usually associated with drier conditions. The wildfire could erupt if there is wind and a forest fire.
(Source : 09-06-2016 Nature World News http://www.natureworldnews.com/articles/ 21710/20160506/canada-wildfires-grown-200-000-acres-thousands-evacuated.htm)

New laws soon for sustainable development
Sri Lanka will soon introduce a new law on sustainable development which will help move the country towards more innovation and future-orientated thinking to inspire better buildings and businesses, Deputy Foreign Minister Dr. Harsha de Silva said.
The new law will come into effect with the launch of the proposed Development Agency. With the introduction of this new law Sri Lanka will become one of the first countries in Asia to legislate sustainable development, Dr. de Silva told Sunday Observer Business.
It is now at the last stage of vetting in the legal draughtsman’s office. “I personally got involved in writing the new law and worked closely with the Attorney General’s department. We wanted to incorporate the objectives of the sustainable development goals.
“What that means is environment and sustainability becomes something that gets incorporated in the body of the text rather than in an appendix. Therefore, green technology is going to be very important in the decisions we make in particular in the megapolis and other urban development projects in Sri Lanka. Clean technology and sustainable development together will help create good and quality jobs which are a major necessity in our country,” Dr. de Silva said. Currently there is no such law or policy in Sri Lanka.
“This move will encourage foreign investments as the investors are assured of a proper monitoring and coordinating body,” he said.
The government is in the process of setting up two key agencies – the Agency for Development and the International Trade Agency.
An International Trade Agency will be set up, with representation of the Foreign Ministry and Export Development Board, and the Department of Commerce.
Sustainable development has become necessary for all economic policymakers and stakeholders at the national and international levels to incorporate the concept of sustainability into their development strategies.

(Green technology – is important in the decisions we make in particular on the megapolis and other urban development project)
In Sri Lanka there are about 87different approvals to be taken from various different organizations prior to launching development projects.
The agency will coordinate and make sure that each individual agency has a plan for their institution.
If it is the Water Board or the Transport Board — whatever it is, we want to ensure they have followed the sustainability laws in their key performance indicators. It will be a monitoring process of sustainable development of the country and responsibilities are entrusted to every organization and investment project.
Parliament has power in ensuring that every investment project is green and sustainable.
(Source 08-05-2016 Sunday Observer-Sri Lanka )

Leopards have lost 75% of their historical habitat
New research shows the big cats’ global range has shrunk by a shocking amount over the last 250 years.
(Photograph: Joseph Lemeris Jr/ZSL)
The area of the world roamed by leopards has declined by three-quarters over the last two and a half centuries, according to the most comprehensive effort yet to map the big cat.
Researchers said they were shocked by the shrinking of the spotted hunter’s range, and that the decline had been far worse for several of the nine subspecies of leopards and in some parts of the world.
“We found the leopard had lost 75% of its historical habitat, we were blown away by that, it was much more than we feared,” said Andrew Jacobson, a conservationist at the Zoological Society of London and lead author of a new study on their range published in the journal PeerJ.
“Our goal has to be to raise consciousness about the plight of the leopard, it’s been flying under the conservation radar for a while. We hoped to raise its profile and say ‘this cat needs your attention’.”
The new work is the first known attempt to draw up a global, historical map of the leopard. Jacobson and researchers found that in 1750 it occupied a vast 35m sq km (13.5m sq mile) area throughout Africa, the Middle East and Asia. But after centuries of habitat loss and hunting caused by humans, that area shrank to just 8.5m sq km.
Leopards in Asia have been particularly badly hit, with six regions losing over 95% of habitat where the species has been, in Jacobson’s view, “almost completely wiped out”.
There appeared to be a clear link between Asia’s economic development and the leopard’s decline there, he said. “South-east Asia and China have been developed for a long period of time and that’s seriously constricted habitat in that area for decades. We worry this will be the trend we will see in Africa in coming decades, as economies grow.”
Even in Africa, the paper found, losses varied greatly, with their range decreasing 99% in North Africa, up to 95% in West Africa but only up to 51% in Southern Africa.
Leopards are a famously reclusive but adaptable species, living nocturnally and hunting a wider variety of prey than other species. They also appear more capable than other big cats at adapting to environments transformed by humans, with leopards living in the outskirts of Mumbai and Johannesburg.
There are no reliable population estimates but it is thought there are over a 100,000 left in Africa and perhaps fewer than 10,000 in Asia.
Jacobson, who is also part of theNational Geographic Society’s Big Cats Initiative, said it was not too late for leopards to bounce back. “I think the leopard can come back. The leopard is an incredibly adaptable animal, we just need to ease off on the hunting pressure, the persecution. They’re cats, they breed pretty well.”
But greater conservation efforts were needed to stop them suffering the dramatic declines seen by some other species, he said. “When people think of endangered animals they think of tigers, elephants, rhino. Thankfully the leopard isn’t in that category yet, and if we are more proactive about them we can stop them being in there.”
The new study – Leopard (Panthera pardus) status, distribution, and the research efforts across its range – examined 6,000 records at 2,500 locations, from over 1,300 sources, including other scientific literature and experts’ data, to draw up a detailed reconstruction of leopards’ range today and in 1750.
(Source : 09-05-2016 The Guardian http://www.theguardian.com/environment/2016/may/ 04/leopards-have-lost-75-percent-of-historical-habitat)

Earth could be Home to 1 Trillion Species
(Rendering of bacterium. The Earth Microbiome Project – a global multidisciplinary project to identify microscope organisms )
The Earth is teeming with life, and apparently humans have only identified one-thousandth of 1 percent of the various species that call the planet home. A new study out of Indiana University, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, reveals that Earth could contain nearly 1 trillion species.
“Estimating the number of species on Earth is among the great challenges in biology,” study co-author Jay T. Lennon, associate professor in the Indiana University Bloomington College of Arts and Sciences, said in a press release. “Our study combines the largest available datasets with ecological models and new ecological rules for how biodiversity relates to abundance. This gave us a new and rigorous estimate for the number of microbial species on Earth.”
The estimate of 1 trillion species was derived from large datasets of recorded plant, microbial, and animal life, from a combination of academic, governmental, and citizen science reports representing more than 5.6 million microscopic and non-microscopic species that exist in 35,000 locations around the world. The researchers call this the largest-ever compilation of such data. All the oceans and continents are represented except for Antarctica.
A big challenge in determining the true number of species on Earth is the fact that it is next to impossible to record all of the forms of microbial life on the planet. “Until recently, we’ve lacked the tools to truly estimate the number of microbial species in the natural environment,” Lennon said. “The advent of new genetic sequencing technology provides an unprecedentedly large pool of new information.”
Simon Malcomber, director of the National Science Foundation’s (NSF) Dimensions of Biodiversity program, stressed that while the study is significant, it highlights just how much life on Earth “still remains to be discovered and described.”
The NSF funded the Indiana University team’s work through a project that aims to “fill major gaps in humanity’s knowledge about the planet’s biodiversity” by 2020, according to the press release. The U.S. Army Research Office also supported the study.
What really differentiates this work is that most studies of life on Earth seemingly ignore microorganisms. Previous efforts to estimate the total number of species on Earth used outdated techniques “or questionable extrapolations,” Lennon said
“Older estimates were based on efforts that dramatically under-sampled the diversity of microorganisms,” Lennon said. But now, advanced genetic sequencing technology can be brought to bear. “Before high-throughput sequencing, scientists would characterize diversity based on 100 individuals, when we know that a gram of soil contains up to a billion organisms, and the total number on Earth is over 20 orders of magnitude greater.”
The study used data from the National Institutes of Health’s Human Microbiome Project, the Tara Oceans Expedition, and the Earth Microbiome Project, among others. The research team pulled together 20,376 surveys of bacteria, archaea and microscopic fungi along with 14,862 sampling efforts on trees, mammals, and birds.
“We suspected that aspects of biodiversity, like the number of species on Earth, would scale with the abundance of individual organisms,” said Kenneth J. Locey, study co-author and a postdoctoral fellow at Indiana University. “After analyzing a massive amount of data, we observed simple but powerful trends in how biodiversity changes across scales of abundance. One of these trends is among the most expansive patterns in biology, holding across all magnitudes of abundance in nature.”
Of course, it is still an overwhelming — if not impossible — task to accurately identify every microbial species on the planet. By comparison, the Earth Microbiome Project has been able to only record 10 million species, so far.
“Of those cataloged species, only about 10,000 have ever been grown in a lab, and fewer than 100,000 have classified sequences,” Lennon stressed. “Our results show that this leaves 100,000 times more microorganisms awaiting discovery — and 100 million to be fully explored. Microbial biodiversity, it appears, is greater than ever imagined.”
(Source 04-05-2016 CBS News http://www.cbsnews.com/news/earth-could-be-home-to-1-trillion-species/)
World Migratory Bird Day
World Migratory Bird Day (WMBD) was initiated in 2006 and is an annual awareness-raising campaign highlighting the need for the conservation of migratory birds and their habitats. Each year, on the second weekend in May.
Why migratory birds?
Avian migration is a natural miracle. Migratory birds fly hundreds and thousands of kilometres to find the best ecological conditions and habitats for feeding, breeding and raising their young. When conditions at breeding sites become unfavourable, it is time to fly to regions where conditions are better.
There are many different migration patterns. The majority of birds migrate from northern breeding areas to southern wintering grounds. However, some birds breed in southern parts of Africa and migrate to northern wintering grounds, or horizontally, to enjoy the milder coastal climates in winter. Other birds reside on lowlands during the winter months and move up a mountain for the summer.
Migratory birds have the perfect morphology and physiology to fly fast and across long distances. Often, their journey is an exhausting one, during which they go to their limits. The Red Knot has one of the longest total migration routes of any bird, travelling up to 16,000 kilometres twice a year. It breeds in Siberia and overwinters on the west coast of Africa, some even going down to the tip of South Africa.
It is truly amazing how migratory birds can navigate with pin-point accuracy. Exactly how migrating birds find their flyways is not fully understood. It has been shown that they are able to orientate by the sun during the day, by the stars at night, and by the geomagnetic field at any time. Some species can even detect polarized light, which many migrating birds may use for navigation at night.
Why Migratory Birds Need Protection
Migration is a perilous journey and involves a wide range of threats, often caused by human activities. And as diverse as people and their habits in different countries are, so are threats the birds face. As migratory birds depend on a range of sites along their distribution area, the loss of wintering and stopover sites could have a dramatic impact on the birds’ chances of survival.
Flying long distances involves crossing many borders between countries with differing environmental politics, legislation and conservation measures. It is evident that international cooperation among governments, NGOs and other stakeholders is required along the entire flyway of a species in order to share knowledge and to coordinate conservation efforts. The legal framework and coordinating instruments necessary for such cooperation is provided by multilateral environmental agreements such as CMS and AEWA.
World Migratory Bird Day has a global outreach and is an effective tool to help raise global awareness of the threats faced by migratory birds, their ecological importance, and the need for international cooperation to conserve them.
The 2016 World Migratory Bird Day Theme
…. and when the skies fall silent? Stop the illegal killing, taking and trade!
So that future generations also benefit from natural resources, governments have passed laws – both domestic and international – to ensure sustainability, protecting wild animals including migratory birds by restricting or prohibiting their exploitation. The protection of migratory birds has been coordinated at the international level since the beginning of the twentieth century. Migratory birds were once synonymous with abundance, and seen as a gift coming from the sky. Historically, people have hunted wildlife for a variety of reasons – food and sport – and in the past, such activities were conducted at a scale that was sustainable. In many cases, however, this is no longer true.
Nets along the north coast of Africa kill millions of birds every year – and it is only one example amongst many. The methods used and the numbers taken have changed beyond measure, and the survival of the targeted species which have to face many other pressures such as loss or deterioration of habitats is in doubt. In many countries, robust legislation exists and mechanisms are in place to enforce it; in others, the rules are not followed and the authorities lack the resources or the will to implement them properly on the ground. If once common migratory birds are to be prevented from disappearing, such as the Linnet that has lost 50% of its population since 1980, or the farmland birds with a loss of 300 million individuals in Europe over the same period, the public has to be made aware of the urgency of the threat posed by illegal hunting, taking and trade. Attitudes must change and we can no longer afford to turn a blind eye to those who flout the law and endanger our shared natural heritage.
There is a wide range of reasons for the illegal killing, taking and trade of birds – subsistence uses, recreational activities, organized crime, traditional practice and so on. They vary from one country to another, from one region of the world to another, according to what has been defined as legal or illegal – if at all. Indeed in some countries there is clearly no regulation, while in others regulations do exist but enforcement needs to be improved. Illegal activities not only affect birds’ populations, but they also harm society in general, our very existence and our natural resources. Conservation, agriculture and the tourism sector all suffer from their negative impacts. Legal hunting is affected by these illegal activities as well: despite the role that hunters play in ensuring the sustainability of livelihoods and habitats, they see their reputation jeopardized by illegal killing. While at the same time, elsewhere in the world, these illegal activities are widely socially accepted and therefore persist. Both at the national and the local level, law enforcement is the key driver to help protecting migratory birds, not only in one place but along their entire flyway.
Cooperation and awareness-raising have to be strengthened in order to fight illegal killing. The Task Force set up by the CMS Secretariat is a first concrete answer to the issue in the Mediterranean region. Further actions are needed – and this shared issue should involve and bring together international organizations, governments and civil society. Indeed decisions taken by the international community or by governments will not meet any success if they are not respected or implemented on the ground. That is where civil society has a role to play, at the local level. Let us work together to protect migratory birds from illegal killing, taking and trade!
(Source 03-05-2015 World Migratory Birdday http://www.worldmigratorybirdday.org/)
Depleted Oxygen in the Ocean Caused by Climate Change Threatens Marine Life

(Photo : Joe Raedle/Getty Images)
The National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) said that by 2030, the ocean might have an alarming level of depleted oxygen which threatens the marine life and human resources as well.
Because of climate change, even the Great Barrier Reef is currently suffering from coral bleaching. But that’s not the only problem caused by climate change. The extreme weather conditions and warmer water also results to the depletion of the oxygen level in the waters.
According to the report by NCAR, “a warming climate can be expected to gradually sap the ocean of oxygen, leaving fish, crabs, squid, sea stars, and other marine life struggling to breathe”. Matthew Long, a scientist at NCAR added “Loss of oxygen in the ocean is one of the serious side effects of a warming atmosphere, and a major threat to marine life.”
Gizmodo also reported the depletion of oxygen level in the ocean. They said that it can be explained by “basic thermodynamics, cold water can hold more dissolved gases than warm water. As our ever-warming atmosphere heats the surface of the ocean, the oxygen content starts to fall. Also, as water warms, it expands and gets lighter. This makes it less likely to sink, which in turn reduces the transport of oxygen from the atmosphere into the deep ocean.”
The problem with depleted oxygen supply is that it greatly threatens marine life. The fishes and other marine animals survive the waters because of the presence of oxygen. Major changes in the environment will affect their ability to thrive.
According to the study published by the Global Biochemical Cycles, the depletion of oxygen in the ocean is already happening, but the most crucial and detectable influence to marine life can be felt by 2030.
They study also states that the oxygen level is important in regulating metabolic and bio-geochemical processes of marine life and the ocean. If the water turns warmer, it will be more difficult for the oxygen to travel deeper, which threatens marine life in deeper sea levels.
Currently, the researchers claim that the deoxygenation in the oceans is already felt in some areas in the world. The study said it is already detected in the southern Indian Ocean and parts of the eastern tropical Pacific and the Atlantic.
The depleted oxygen level in the ocean which threatens the marine life should be reason enough for mankind to try and curb climate change. If it does transpire in 2030, it won’t just affect marine life but the natural cycle in life. Imagine how a dead ocean ecosystem affects the livelihood and resources of men.
(Source :01/05/2016 :Nature World News http://www.natureworldnews.com/articles/21378/20160430/depleted-oxygen-in-the-ocean-caused-by-climate-change-threatens-marine-life.htm)
Depleted Oxygen in the Ocean Caused by Climate Change Threatens Marine Life

(Photo : Joe Raedle/Getty Images)
The National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) said that by 2030, the ocean might have an alarming level of depleted oxygen which threatens the marine life and human resources as well.
Because of climate change, even the Great Barrier Reef is currently suffering from coral bleaching. But that’s not the only problem caused by climate change. The extreme weather conditions and warmer water also results to the depletion of the oxygen level in the waters.
According to the report by NCAR, “a warming climate can be expected to gradually sap the ocean of oxygen, leaving fish, crabs, squid, sea stars, and other marine life struggling to breathe”. Matthew Long, a scientist at NCAR added “Loss of oxygen in the ocean is one of the serious side effects of a warming atmosphere, and a major threat to marine life.”
Gizmodo also reported the depletion of oxygen level in the ocean. They said that it can be explained by “basic thermodynamics, cold water can hold more dissolved gases than warm water. As our ever-warming atmosphere heats the surface of the ocean, the oxygen content starts to fall. Also, as water warms, it expands and gets lighter. This makes it less likely to sink, which in turn reduces the transport of oxygen from the atmosphere into the deep ocean.”
The problem with depleted oxygen supply is that it greatly threatens marine life. The fishes and other marine animals survive the waters because of the presence of oxygen. Major changes in the environment will affect their ability to thrive.
According to the study published by the Global Biochemical Cycles, the depletion of oxygen in the ocean is already happening, but the most crucial and detectable influence to marine life can be felt by 2030.
They study also states that the oxygen level is important in regulating metabolic and bio-geochemical processes of marine life and the ocean. If the water turns warmer, it will be more difficult for the oxygen to travel deeper, which threatens marine life in deeper sea levels.
Currently, the researchers claim that the deoxygenation in the oceans is already felt in some areas in the world. The study said it is already detected in the southern Indian Ocean and parts of the eastern tropical Pacific and the Atlantic.
The depleted oxygen level in the ocean which threatens the marine life should be reason enough for mankind to try and curb climate change. If it does transpire in 2030, it won’t just affect marine life but the natural cycle in life. Imagine how a dead ocean ecosystem affects the livelihood and resources of men.
(Source :01/05/2016 :Nature World News http://www.natureworldnews.com/articles/21378/20160430/depleted-oxygen-in-the-ocean-caused-by-climate-change-threatens-marine-life.htm)

How Climate Change Affects Ocean’s Oxygen Level
The continues global warming due to climate change has been known to take its toll to Arctic, melting ice caps at an increased rate, but a new study suggests that the warming climate may be sapping considerably amounts of oxygen from the ocean.

(Photo : Lam Yik Fei/Getty Images)
According to the study published in the journalProceedings of the Royal Society B, scientist have long known that the warming climate can sap oxygen from the ocean, but they have discovered that a considerable amount of oxygen reduction in some oceans are already discernable, and by 2030 and 204 the loss of oxygen level across large oceans around the world will become more apparent.
With the reduction of the ocean’s oxygen level, marine species such as fishes, crabs and squids will have more difficulty of breathing, which can result to the sudden death and development of larger dead zones where no marine life can live.
“Loss of oxygen in the ocean is one of the serious side effects of a warming atmosphere, and a major threat to marine life,” said NCAR scientist Matthew Long, lead author of the study, said in a statement.
If the atmosphere becomes warmer than usual, oceans ability to draw oxygen from the atmosphere will be inhibited leaving it dependent to its other source of oxygen-the photosynthesizing phytoplankton.
In order to have a better grasp in the natural heating and cooling cycles and complex systems of currents and upwelling of oceans, researchers utilized the National Center for Atmospheric Research’s (NCAR) Community Earth System Model. They ran the model multiples times for the years 1920 through 2100. The researchers accounted global warming by making slight manipulations in air temperature.
After running the model, researchers identified that the reduction of oxygen in the ocean that can be attributed to global warming is apparent in 2030.
“Since oxygen concentrations in the ocean naturally vary depending on variations in winds and temperature at the surface, it’s been challenging to attribute any deoxygenation to climate change. This new study tells us when we can expect the impact from climate change to overwhelm the natural variability,” Long concluded.
(Source : 29/04/2016 Nature World News http://www.natureworldnews.com/articles/21285/20160428/climate-change-affects-ocean-s-oxygen-level.htm)




