Govt okays electric fences around waste dumps to save elephants
by Chaminda Silva
Cabinet approval has been granted for erecting electric fences to prevent wild elephants from entering 54 waste disposing dumps located in wildlife zones.
The project has been proposed jointly by Minister of Sustainable Development and Wildlife Gamini Jayawickrama Perera and Minister of Provincial Councils and Local Government Faizer Mustapha to implement a waste recycling programme, giving priority to such wildlife zones.
Improper waste disposal has impacted badly on the environment as well as animals, especially elephants and therefore measures would be taken to implement a waste recycling programme in areas where wild elephants were roaming to protect them, the government said.
There are 54 waste disposing dumps located in wildlife zones and about 300 wild elephants are loitering around those dumps. The government said local authorities would be banned from dumping solid waste in the open.
source – 1/06/2017,The Island, see more at – http://www.island.lk/index.php?page_cat=article-details&page=article-details&code_title=166046

World Environment Day 2017: Connecting People to Nature
World Environment Day – which is observed on 5 June every year across the globe – is the largest annual event for positive environmental action.
World Environment Day was inaugurated in 1972 following the United Nations Conference on the Human Environment in Stockholm, Sweden on 5-16 June – the first international conference on environmental issues.
Since its first celebration on 5 June 1974, millions of people across the world have taken part in thousands of events to raise awareness and generate political momentum around growing concerns such as the depletion of the ozone layer, toxic chemicals, desertification and global warming.
Events range from neighbourhood clean-ups, to action against wildlife crime, to replanting forests.
The Day has developed into a global platform for taking action on urgent environmental issues, driving change in our consumption habits as well as influencing national and international policy.
The host country for this year’s celebration is Canada, succeeding 2016 host Angola.
Canada has chosen the theme “Connecting People to Nature” for 2017, which invites people to enjoy the outdoors and to take forward the call to protect the Earth that we share.
Erik Solheim, Head of UN Environment, said: “It reminds us of what a treasure nature is, and encourages us all to protect and appreciate our environment.”
Countries around the world will host events and introduce initiatives to celebrate the largest annual event for positive environmental action.
This year the citizens of Mumbai, India are taking part in a mass beach clean-up, while Canada is offering free entry to its national parks and marine conservation areas.
To get involved you can join the global album by sharing a photo or video of your favourite place in nature using #WorldEnvironmentDay or #WithNature.
You can also join over 1,000 events taking place across the globe, or even organise your own.
Or why not help build the world’s largest nature database by recording the wonders of biodiversity in your local environment.
World Environment Day has partnered with the iNaturalist global network to record all contributions, which will be shared with scientific data repositories.
Source – 1/06/2017,ClimateAction, See more at – http://www.climateactionprogramme.org/news/world-environment-day-2017-connecting-people-to-nature

Waste and affluence: More money, more garbage
 The catastrophe that was Meethotamulla in mid-April during what should have been a joyous time of anticipating a New Year was a stark warning of a serious man-made disaster that can recur, not just in Kolonnawa but in other areas as well.
The catastrophe that was Meethotamulla in mid-April during what should have been a joyous time of anticipating a New Year was a stark warning of a serious man-made disaster that can recur, not just in Kolonnawa but in other areas as well.
Smaller dumps due to indiscriminate dumping can be seen rising up in various parts of the country while “sili sili” bags hanging off thorny bushes, glistening silver wrappers amongst the water lilies, multi coloured plastic pieces scattered on the beaches are becoming part of our natural scenery. We are caught in a paradox of a more affluent country drowning in garbage.
Solid waste and affluence have a positive co-relationship. Studies show that as societies become wealthier, they generate more food waste (organic) as well as more non-organic items such as paper and plastic packaging, electronic waste etc. The less affluent are much better recyclers – out of necessity. Thus, more disposable income results in more “disposable” products.
A World Bank study aptly titled “What a waste” claims that not just affluence but urban living also leads to more solid waste. The report estimates that by 2025, 4.3 billion urban residents will generate about 1.42 kg of solid waste per capita per day. Solid waste management is one of the largest recurring costs for municipal and urban authorities and the cost is said to see a four-fold (or more) increase in lower-middle income countries in the next decade. Although this study, conducted in 2012, says that South Asia is one of the regions generating the least waste, this trend will change, with projected increase in urbanisation and incomes. So how will we manage our waste?
Solid waste management is a pressing environmental problem. It is assumed that the prime responsibility of waste management rests squarely on the authorities that are supposed to manage waste. After all, as residents, we pay taxes and it is the job of the local authority to have systems in place and planned living spaces with adequate attention to waste disposal. While it is of utmost importance that waste management systems are in place, does it not also warrant some sort of action from us, the ones generating the garbage? 
Our current growth model is run on consumption, and wellbeing is heavily reliant on material things. We do not worry too much about what we spew out as waste into the environment. This mode of operating is a crucial factor driving climate change as we are emitting more waste than the environment can absorb. Eventually this will come back to bite us. As is the case with most things related to climate change, it can also affect those who had the least to do with the problem.
Hence a new way of thinking or bringing back an old concept of growing within our means is needed. This requires thinking of the production cycle like a closed system (circular economy), where natural resources are used and reused to the maximum and what needs to be managed as waste is minimised. Some companies have proactively sought to adopt these approaches but such practices are yet to be fully embraced in our society. Other ideas that are slowly emerging are for consumers to rent or lease products and give it back to be ‘transformed’ into new products. Thus, cutting out waste and also reorienting the idea of ownership.
Garbage also has external costs such as illnesses and increased cost of living but also infringes on the rights of people to live in a clean and healthy environment. These are also the reasons why we need to go that extra mile and reflect on our own consumption patterns. So in our quest for more affluence, a more conscious effort is needed to guide us on what we throw away.
The fundamental for waste management from a consumer end is separation of garbage but also minimization of garbage. It is not as if we have to learn or be taught about minimising waste from scratch. Traditionally, people would recycle – from glass bottles to jam jars to used clothes and kitchen waste. We are also seeing so many more creative ways in which waste from one source can be “upclycled” or converted into something else. It will not happen overnight and much effort is needed – but it is also in our best interest for a healthier life. Hence, in this post-Meethotamulla debate about waste management, while we badly need better waste management services, it is also important to rethink what we consider waste and to put more emphasis on the individual’s responsibility towards minimising waste.
This would be the citizen’s contribution to wellbeing.
Source – 28/05/2017, The Sunday Times, See more at – http://www.sundaytimes.lk/170528/business-times/waste-and-affluence-more-money-more-garbage-242361.html
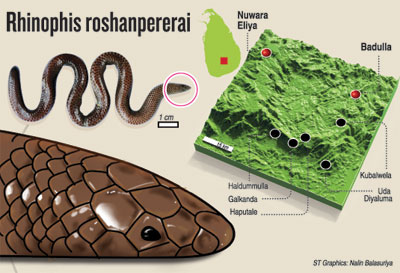
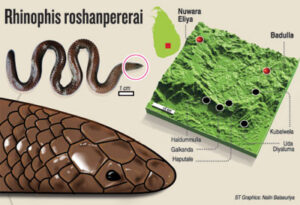
Roadkill leads to discovery of burrowing snake
A new burrowing snake was added to the list of species endemic to Sri Lanka when International Day of Biological Diversity was marked on Monday, strengthening the country’s image as a biodiversity hotspot.

A new non-venomous ‘shield tailed snake’ that lives under the soil was discovered from the Badulla District. The scientific paper describing this new species appeared in prestigious scientific journal ZooTaxa.
The new species is yet another discovery by veteran herpetologist Mendis Wickremasinghe, who recalls that he first saw the snake as a single roadkill specimen in 1999 in Beragala. Later, during an island-wide herpetology survey, Mr Wickremasinghe decided to search the area.
 The researchers dug randomly selected locations that are habitats for such species. They got lucky and found a snake hidden under the soil layer of a banana plant of a home garden in 2010. The snake was found about 15 centimetres deep and had a highly-modified head, bearing a blade-like rostral scale for burrowing.
The researchers dug randomly selected locations that are habitats for such species. They got lucky and found a snake hidden under the soil layer of a banana plant of a home garden in 2010. The snake was found about 15 centimetres deep and had a highly-modified head, bearing a blade-like rostral scale for burrowing.
Mr. Wickremasinghe said about 30 individuals could be observed during subsequent visits to the same locations. More such snakes were observed from the same locality and in suburban areas like Haldummulla with some of them seen moving above ground at night.
With the new discovery, this rhinophis genus now has 20 such snake species with 16 of them found in Sri Lanka that are endemic to the country. The other four snakes are endemic to India. Three of these Sri Lankan species have been recently described in 2009 and 2011. Mr Wickremasinghe said there could be more snake species that belongs to this group, emphasising need for more studies.
Dulan Ranga Vidanapathirana and Gehan Rajeev too assisted in this new finding. Mr Wickremasinghe also thanked the principal sponsors, Dilmah Conservation.
Source – 28/05/2017,The Sunday Times, Read more at – http://www.sundaytimes.lk/170528/news/roadkill-leads-to-discovery-of-burrowing-snake-242678.html

Sinharaja elephant attacks raise villager fury
The recent photograph that shows an elephant in musth
By Malaka Rodrigo
Sri Lanka’s biodiversity hotspot, Sinharaja, is home to two elephants – but pressure is mounting to translocate them after one killed two villagers. Last week, some angry villagers demanded the elephants be removed as a man and a woman were killed in Cypresswatte village.
The incident happened on May 16. The woman was killed at about 6:45 p.m., while the man was fatally attacked around 8 p.m.
A few days earlier, on May 13, the same elephant attacked a Wildlife Department jeep when the vehicle was involved in chasing the animal back into the forest. This incident was near Kudawa, Weddagala around 8.30 p.m. The panicked animal turned back and crushed the bonnet of the vehicle, slightly injuring those inside.
The elephant had been seen at other locations. It had paced around the tower on top of the Gongala Mountain. A photo taken at Gongala shows the elephant is in musth, which is the periodical rise of reproductive hormones of a bull elephant. At such times the animals are irritable and aggressive.
According to DWC records, the two Sinharaja elephants are responsible for 16 human deaths in villages such as Kopi-kella, Manikkawatte and Cypresswatte. Tea cultivations block their natural passages, forcing them to sometimes wander into populated areas.
Madura De Silva, the president of the Wildlife Conservation Society of Galle, said that there were three elephants sometimes back – one female and two males. The society setup camera traps as a part of a project related to leopards and the cameras captured the movements of an elephant. With the data they mapped its range.
DWC director general, W S K Pathiratne, said a decision had not been taken yet to translocate the killer elephant. More wildlife officers will be sent to the are.
 When asked if a radio collar could be fitted to track the animal, he said trapping the elephant would be challenging in the difficult terrain.
When asked if a radio collar could be fitted to track the animal, he said trapping the elephant would be challenging in the difficult terrain.
The elephant was in fact caught in 1999 by a team led by Dr Nandana Atapattu – a veterinary surgeon who was also a deputy director of DWC then. It took a team of 20 and a week-long effort. But villagers at the time, particularly the students of Kajuwatta School protested against removing the elephant saying it was an asset to the area. Dr Atapattu released the elephant.
At that time, there were records that the elephant charged but did not kill anyone.Environmentalist Jayantha Wijesinghe said these elephants roamed widely around Sinharaja, but attacked people only in some places. “The reason being that the villagers in these areas have harmed the duo, so the elephants become more aggressive,” he said.
The president of the Wildlife Conservation Society of Galle, Mr De Silva, said that in many areas, the local villagers understand the elephant’s movements and that helps to avert a potential disaster. He also said that because of the elephants, illegal activities such as felling trees for ‘walla patta’ and gem mining has been under control. “These elephants are the jewels of Sinharaja. it is better to let them be.”
The Sinharaja rainforest is a UNESCO World Heritage Man and Biosphere Site.
Source – 28/05/2017, The Sunday Times , Read More at – http://www.sundaytimes.lk/170528/news/sinharaja-elephant-attacks-raise-villager-fury-242684.html

Analog Forestry Project in Belipola, Mirahawattha
(Courtesy of UN-REDD)
As we all agree on the importance of development in Sri Lanka, we must also recognize its current destruction of our natural resources. We have trampled down many of our precious resources in the name of progress. Will we be able to restore the forest resources that have benefitted us so much thus far?
As many as 52 years ago the rapid consumption of our forests was predicted by a Sri Lankan Student named Ranil Senanayake. He decided that the disappearance of our forests would eventually need to be answered through a system of analog forestry.
In about 1965 analog forestry was thought up from a concern for rapdily vanishing birds, snakes, and butterflies that were once so common. He noted an answer in ancient home-gardens which are rich in biodiversity. In an analog forest vegetation is specifically chosen to promote biodiversity and to fit together like pieces of a puzzle to meet the needs of a biodiversity hotspot. The analog forest will provide a farmable crop while boasting an exquisitely biodiverse habitat. It’s like intentionally building a forest to grow a desired set of vegetation to meet your needs.
The blueprint starts with the area’s natural forest. It is the basis of a forest that should be created in a farm. By studying different forests at different stages of maturity the roadmap to the final structure could be sketched out.
In 1978 upon receiving a doctorate in System Ecology he started his own experiments with analog forestry in his forest institute at ‘Belipola’, Mirahawatthe, Bandarawela. Trials and researches at Belipola Estate were very promising. On the sixth year the Export Crop Department declared that the ‘experimental one acre plot’ of Belipola has adequate canopy closure, humic soil, and air moisture to grow cardamom in an integrated setting. This is a remarkable feat from the barren land they started with. Also, many unique types of tree frogs and forest fauna migrated in to this former scrub land. Today, Belipola has reached a milestone in analog forestry boasting a prime teaching example for how great the benefits of analog forestry can be. Dr. Senanayake regularly holds workshops in Belipola and abroad. His expertise in analog forestry can be used to create well complimented forests, and to avoid many pitfalls along the way.
Farming via analog forestry produces multiple crops that can be harvested throughout the year. This approach to farming can create a far more stable income for farmers. Analog forestry for farming takes careful preparation and planning, but can yield substantial incomes as well as creating an environment for biodiversity to thrive.
Analog forestry is now a mainstream subject in many universities in Sri Lanka and abroad. Tropical countries are extending analog forestry training to farmers to encourage these practices. In Sri Lanka analog forestry is being applied in numerous villages. In 1996 the Environment Liaising Center International (Nairobi) and Both-Ends (The Netherlands) accepted analog forestry as their institutional responsibility.
Many global institutes are on a forward marching restoring the world’s ecosystems from such pressing issues. Sites like these are supported by the UN-REDD program. UN-REDD is the worldwide movement to reduce emission of greenhouse gases due to degradation and destruction of forests. Local communities worldwide can see great benefits from being directly involved with REDD+ activities. To learn more visit reddpluslk.com.
Source – 28/05/2017, The Island , See more at – http://www.island.lk/index.php?page_cat=article-details&page=article-details&code_title=165850

Sri Lanka approves hybrid renewable energy project
Sri Lanka’s Cabinet of Ministers has given the green light to the development of a hybrid renewable energy project in Punarin, which includes 240 megawatts (MW) of wind and 800 MW of solar.
The move is in line with the Sri Lankan government’s plans to significantly expand renewable energy sources’ share of the nation’s power mix.
The Sri Lanka Sustainable Energy Authority (SLSEA) has identified the northern regions of the country as a suitable location to construct wind and solar power plants.
Under the proposal, the construction of the hybrid energy park will be built in three phases spanning two years.
The government recently unveiled its policy to add a considerable amount of electricity to the national grid through renewable energy sources.
Ceylon Electricity Board has set a target to increase electricity produced by renewables from the 10 per cent generated today, to 17 per cent by the end of 2019.
In March, the Cabinet announced the nation will issue an international tender to set up a 100 MW floating solar plant on the Maduru Oya Reservoir, in the east of the country.
Since then, Sri Lanka has announced it will allocate LKR350 million (US$2.29m) in the 2017 budget to implement its green building policy.
Source – 25/05/2017,Climate Action, See more at – http://www.climateactionprogramme.org/news/sri-lanka-approves-hybrid-renewable-energy-project

Dead Jumbo’s stomach contained 25kg polythene
The stomach of a dead wild elephant was found to contain over 25 kg of polythene, according to Wild Life officials in the Polonnaruwa District.
A wild elephant was found dead on the main road between Polonnaruwa and Batticaloa yesterday (24). It had fallen on a garbage dump which contained polythene bags and plastic bottles.
The Wild Life officials, who went to the scene to examine the carcass of the elephant, carried out an autopsy with the help of a veterinary surgeon, sources said.
The surgeon who had performed the autopsy at the spot where the animal had collapsed found polythene weighing 25kg in its stomach sources added.
Further examination confirmed that the dead elephant was 30 years old.
The Wild Life officials said that due to garbage being dumped on the roadside wild elephants come out of the forests to eat the waste.Despite the elephant –human conflict in the Eastern Province having led to the death of elephants and humans on a large scale, the new phenomenon is the death of wild animals due to the consumption of polythene and plastic waste dumped on the roadsides in the jungle areas.
The Wild Life officials had also confirmed that in recent times nearly eleven elephants had died due to consuming the polythene and plastic waste dumped on the roadside.
Source – 25/05/2017,Ceylon Today, See more at – http://www.ceylontoday.lk/article20170401CT20170930.php?id=5204

World is home to ‘60,000 tree species’
There are 60,065 species of trees in the world, according to a comprehensive study of the world’s plants. Botanical Gardens Conservation International compiled the tree list by using data gathered from its network of 500 member organisations. It hopes the list will be used as a tool to identify rare and threatened species in need of immediate action to prevent them becoming extinct. Details of the study appear in the Journal of Sustainable Forestry. The data revealed that Brazil was the nation with the greatest number of tree species, home to 8,715 varieties.
Source – ITN News, Read more at – https://www.itnnews.lk/world-news/world-is-home-to-60000-tree-species/

Snail’s DNA secrets unlocked in fight against river disease ? 1617 readers have read this article !
Scientists have decoded the genome of a snail involved in the spread of a deadly parasitic disease.
They say the information will help in the fight against schistosomiasis, an infection caused by a parasitic worm that lives in streams and ponds.
The disease affects millions of people a year in sub-tropical and tropical regions.
More than 100 researchers from around the world have unlocked the DNA secrets of a snail that transmits the parasite.
They say it will help in the understanding of the snail’s biology, including new ways to stop the parasite spreading to people.
“Having the knowledge means we can progress at a much faster pace at understanding the disease and reducing the number of people infected,” said Dr Joanna Bridger of the University of Brunel, a co-researcher on the study.
The snail (Biomphalaria glabrata) is found in South America.
Related snails are responsible for transmitting the parasite in sub-Saharan Africa, where most cases occur.
People become infected when larval forms of the parasite – released by freshwater snails – penetrate the skin in contaminated water.
In the body, the larvae develop into adult worms, which live in the blood vessels and release eggs.
Some of the eggs are passed out of the body to continue the parasite’s lifecycle.
Others become trapped in body tissues, causing damage to organs.
There is no vaccine for schistosomiasis and current control measures involve mass administration of the drug, praziquantel.
Scientists now hope to develop new treatments, perhaps by disrupting the snail’s mating habits.
The information will also be useful in tracking snail populations that differ in how they transmit the parasites.
“This work provides several inroads for control of Biomphalaria snails to reduce risks of schistosome (re) infection of endemic human populations, an important component of the WHO strategy aimed at elimination of the global health risks posed by schistosomiasis,” said the researchers in the journal, Nature Communications.
The research was led by Prof Coen Adema from the University of New Mexico.
Several UK research teams were involved, including the universities of Brunel, Aberdeen, Aberystwyth, Westminster, Kingston, Oxford, and the Natural History Museum.
Source – Ceylon Today, See more at – http://www.ceylontoday.lk/article20170401CT20170930.php?id=5134