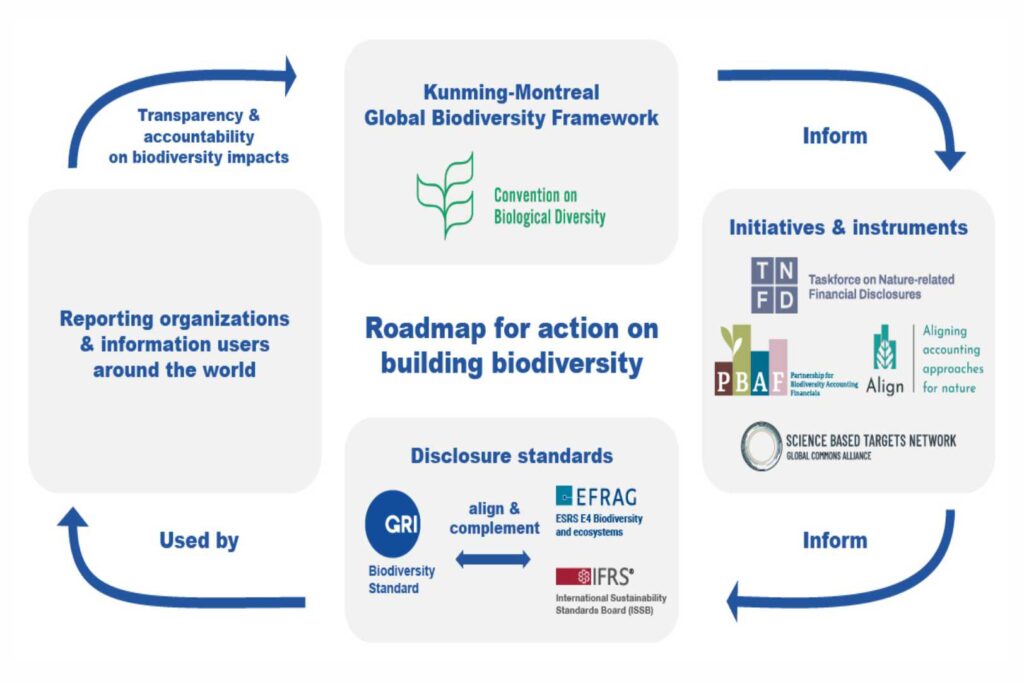
Biodiversity reporting has become a critical focus for businesses, especially in light of new international regulations. The Global Data and Biodiversity Framework (GDF), established at COP 15, emphasises the importance of understanding various regulations, such as the EU’s Deforestation Regulation, which directly impacts supply chains. Companies involved in exports must prepare for due diligence regarding their biodiversity impacts, ensuring compliance with these emerging standards.
Many organisations face significant challenges in data collection and reporting, which are essential for demonstrating their sustainability efforts. To address these challenges, tools like the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) and the Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD) are recommended to enhance reporting practices and ensure transparency in operations.
Implementing Initiatives
Financial implications are also paramount, as businesses will need to account for their ecological impacts in financial statements. The upcoming International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) will require companies to quantify their biodiversity dependencies and impacts, making proactive environmental management crucial. Current actions taken by businesses will shape future reports, highlighting the importance of long-term planning.
Successful examples of companies implementing biodiversity initiatives illustrate that collaboration across sectors is vital for effective biodiversity management. Addressing biodiversity is not just a regulatory requirement; it also presents an opportunity for businesses to showcase their commitment to sustainability.
Impacts and Dependencies
Key frameworks like the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD) can help businesses identify and assess nature-related risks and opportunities. TNFD’s integrated approach for the identification and assessment of nature-related issues called the LEAP approach is designed for use by organisations of all sizes and across all sectors and geographies. By employing a LEAP framework, companies can better understand their impacts and dependencies on biodiversity.
Globally, businesses are urged to adopt comprehensive reporting practices and engage in collaborative efforts to enhance resilience while contributing positively to environmental conservation. By understanding their value chains and interactions with nature, companies can effectively manage risks associated with biodiversity loss while seizing opportunities for sustainable growth.



